
[ad_1]
Classification of fires and types of fire extinguishers on board of merchant ships
CONTENT :
Types of fire extinguishers
Classification of fires:
Class A – Combustible materials
Class B – Flammable liquids
Class C – Flammable gases
Class D – Flammable metals
Class E – Electrical fire
Class F (K) – Cooking oils and fats
Different kind of extinguishers that must be used to resist each type of fire
Table visualizing usage of different fire extinguishers in different types of fires
List of suppliers of fire-fighting equipment and fire-fighting service providers
Everyone knows what a fire phenomenon is. Fire is the process of combustion of inflammable materials producing heat, light and smoke. We use it every day to heat our homes and cook our meals. But when fire is uncontrolled it can totally destroy whatever lies on its path.
When fire occurs on board of seagoing vessel it can result in disaster. Modern vessel is a sophisticated structure with a great number of combustible materials and equipment not to mention oil tankers and gas carriers which carry thousands tons of dangerous fuel. Needless to say that fire on such vessels would result in catastrophic consequences.
In order to prevent fire on board there a number of certain requirements issued by international regulatory authorities which must be followed on each vessel.
There are fixed fire extinguishing systems and portable extinguishers on board a vessel. In this article we will focus on portable ones.
Types of fire extinguishers
There are several types of fire extinguishers depending on the extinguishing agent:
- Water fire extinguisher
- Foam fire extinguisher
- Wet chemical fire extinguisher
- Dry powder fire extinguisher
- Сarbon dioxide (CO2) fire extinguisher
All fire extinguishers are designed to resist specific types of fire. There are six different classes of fire:
- Class A – Combustible materials
- Class B – Flammable liquids
- Class C – Flammable gases
- Class D – Flammable metals
- Class E – Electrical fire
- Class F (K) – Cooking oils and fats
Classification of fires
Class A – Combustible materials
Fire Class A involves wood and wood-based materials, textiles and fibers, plastics and rubber.
These can be facing materials, moldings, decorations, plywood, furnishings, sofas, chairs, tables, curtains, television sets, books, dunnage materials, staging and other items.
These materials may be located in bridge, carpenter’s shop, boatswain’s locker, bridge wing emergency locker, crew cabins and others.
Class B – Flammable liquids
Fire Class B involves flammable liquids.
Flammable liquids may involve heavy fuel oil, diesel oil, lubricating oil, hydraulic oil. Also flammable liquids carried as cargo by tankers and flammable liquids in smaller packages in holds of vessels carrying dangerous goods, as well as dangerous liquids carried by vehicles in tanks. Paints, varnishes and some kinds of enamels present a high fire risk in storage or in use.
These materials may be located in engine room, galley, machinery spaces, mechanics shops and spaces where lubricating oils are used, cargo tanks.
Class C – Flammable gases
Fire Class C involves flammable gases.
Flammable gas can be considered any gas that will burn when mixed with oxygen in air in the right proportions. Examples of flammable gases are: hydrogen, butane, methane and ethylene. There are usually three ways to store and transport flammable gases onboard vessel: compressed, liquefied and cryogenic.
Different mixtures of gases are commonly used on board a vessel for calibration of different equipment and can be found in engine room and machinery departments compressed in cylinders. Also modern tanker vessels transport LNG (liquefied natural gas) using LNG as a fuel as well.
Class D – Flammable metals
Fire Class D involves metals.
Every modern ship is made of metal and different kinds of alloys. Although metals are commonly non-flammable in its nature, however they can contribute to fires and fire hazards. Sparks from the ferrous metals, iron and steel, can ignite nearby combustible materials. Also divided metals are easily ignited at high temperatures and are subject to self-heating under certain conditions resulting in fires.
Metals can be found everywhere on board. Hull, superstructure, all the cabins, departments are made of metal on board of a merchant ship. Container ships carry thousands of metal and aluminum containers, as well as millions tons of metal goods in bulk are carried by general cargo vessel all around the world.
Class E – Electrical fire
Fire Class E involves electrical equipment such as electric motors, generators, switches, panel boards, electric instruments, computers etc.
Nowadays there are many electric equipment can be found on board any type of vessel. Such equipment can be found in engine room, cargo control room, engine control room, crew cabin, galley, bridge and others.
Class F (K) – Cooking oils and fats
Fire Class F (K) involves cooking oils in well-insulated cooking appliances.
Class F fires involve cooking oils, cooking grease and fats. Class F is used in European countries and in Australia and Asian countries while Class K is used in under American system.
While cooking oils can be defined as a subclass of flammable liquid, due to higher flash point they were extracted into separate fire class.
Generally cooking oils, greases and fats exist in ship’s galley and pantry. There are different griddles, fat fryers, oven, stoves on board accumulating cooking oils, grease and fats near to cooking place.
Different kinds of extinguishers that must be used to resist each type of fire dpending on fire class
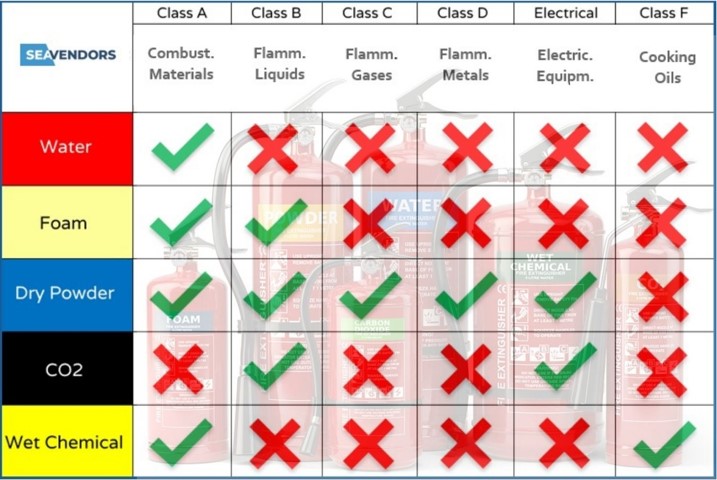
So which kind of extinguisher must be used to resist each type of fire? Here is the list of fire classes along with proper extinguishers to use:
Class A – Combustible materials: Water, foam, dry powder and wet chemical extinguishers
Class B – Flammable liquids: Foam, dry powder and CO2 extinguishers
Class C – Flammable gases: Dry powder extinguishers
Class D – Flammable metals: Dry powder extinguishers
Class E – Electrical fire: Dry powder and CO2 extinguishers
Class F (K) – Cooking oils and fats: Wet chemical extinguishers
Table visualizing usage of different fire extinguishers in different types of fires
Useful links:
Permanent link to this article: Classification of fires and types of fire extinguishers on board of merchant ships
[ad_2]
This article has been posted as is from Source