
[ad_1]

NYK Line, Japan Engine Corporation, IHI Power Systems Co., Ltd., and Nihon Shipyard Co., Ltd. (i.e., “the Companies”) are pleased to announce that Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) has approved the Companies’ participation in a demonstration project for the commercialization of vessels equipped with a domestically produced ammonia-fueled engine as part of the Green Innovation Fund project.*
The demonstration project, which is scheduled to begin in December with ClassNK added to the Companies, aims to use ammonia as fuel to significantly reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions during voyages and thus introduce an ammonia-fueled vessel for the good of society earlier than 2030. The Companies will eventually work toward the goal of achieving zero emissions from ships in the future.
Target
The Companies and ClassNK’s greatest goals are to realize the development of an ammonia-fueled vessel that is internationally competitive ahead of other countries and to lead the development of safety guidelines and laws and regulations related to ammonia-fueled vessels. In order to achieve these goals, marine engine manufacturers, shipyards, class societies, and shipping companies in Japan will work together to consistently cooperate from the research and development stage to engine development, shipbuilding, and commercialization.
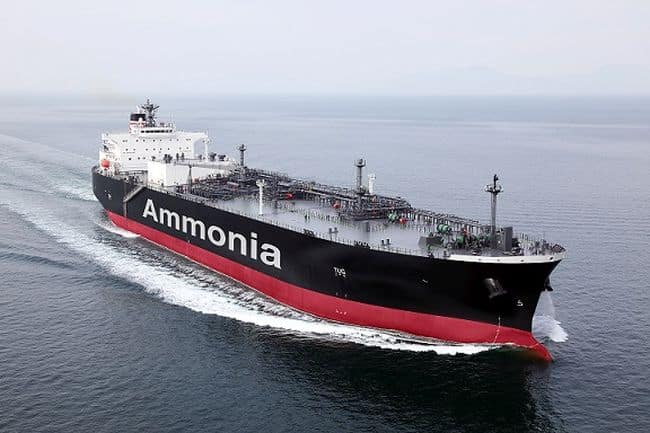

Image Credits: nyk.com
Background
With the entry into force of the Paris Agreement in 2016, the global momentum for decarbonization is increasing. The Japanese government has declared that it will reduce GHG emissions to zero as a whole by 2050 and aim for carbon neutrality, and the energy shift toward the realization of a carbon-free society is accelerating.
Reducing GHG emissions is also an urgent issue in the shipping industry, and research and development are being conducted to convert marine fuel from conventional heavy fuel oil to liquefied natural gas (LNG) and to popularize next-generation zero-emission fuels such as hydrogen and ammonia.
Ammonia does not emit carbon dioxide (CO2) even when burned, so it is expected to be a next-generation fuel that contributes to global warming countermeasures. Furthermore, it is said that by utilizing CO2-free hydrogen** for hydrogen, which is the raw material for ammonia, it is possible to achieve zero emissions in consideration of the fuel life cycle.

Image Credits: nyk.com
Under this background, Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry started the Green Innovation Fund project toward carbon neutrality by 2050, and NEDO has now approved the Companies’ development of vessels equipped with a domestically produced ammonia-fueled engine as part of the Green Innovation Fund project.
Overview of the demonstration project and the roles of Companies
NEDO has approved these demonstration projects, (1) the development and operation of an ammonia-fueled tugboat and (2) the development and operation of an ammonia-fueled ammonia gas carrier, and the companies will carry them out.
(1) Development and operation of an ammonia-fueled tugboat (A-Tug)
The ammonia fuel will have a flame retardant bottleneck, which is difficult to ignite, so this project assumes that a small amount of fuel oil will be used as pilot fuel. Targeting the delivery of A-Tug in FY2024, the companies aim to reduce GHG emissions by achieving an ammonia fuel mixed combustion rate of 80% or higher.
The companies will confirm safe operation in demonstrations aimed to improve the mixed combustion rate with a view to achieving zero GHG emissions by using biofuel as a pilot fuel in the future.
| NYK Line | Project management, ship design and legal compliance |
| IHI Power Systems Co., Ltd. | Research and design of four-stroke engine*** |
| Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK) | Safety assessment of A-Tug |
(2) Development and operation of an ammonia-fueled ammonia gas carrier (AFAGC)
Targeting the ship’s delivery in FY2026, the Companies will develop and operate an ammonia-fueled ammonia gas carrier (AFAGC) with the concept of transporting ammonia as cargo and using the cargo and ammonia gas vaporized from the cargo as fuel during the voyage.
The Companies aim to reduce GHG emissions by achieving a maximum ammonia fuel mixed combustion rate of 95% for the main engine that moves the ship, and an ammonia fuel mixed combustion rate of 80% or more for the auxiliary engine that runs the generator.
| NYK Line | Project management, ship design and legal compliance |
| Japan Engine Corporation | Research and design of two-stroke engine (main engine)**** |
| IHI Power Systems Co., Ltd. | Research and design of four-stroke engine (auxiliary engine) |
| Nihon Shipyard Co., Ltd. | Development of hull, examination of ship construction method |
| Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK) | Safety assessment of AFAGC |
Schedule
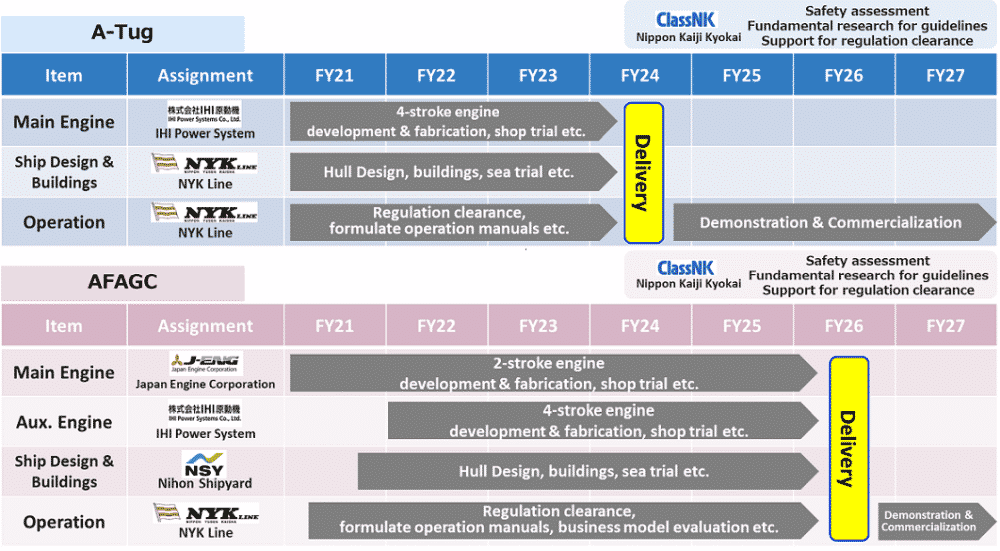
Click To Enlarge | Demonstration project schedule
* Green Innovation Fund project
A 2 trillion yen fund created in NEDO to significantly accelerate current efforts such as structural transformation of the energy and industrial sector and innovation through bold investment toward carbon neutrality by 2050. The fund provides continuous support from R&D and demonstration to social implementation for up to 10 years for companies that share ambitious and concrete goals with the public and private sectors and tackle them as management issues. NEDO provides support mainly in 14 priority areas for which action plans are being formulated in the green growth strategy.
** CO2-free hydrogen
One way of producing hydrogen without generating CO2 is through the use of renewable energy. A second way is by using natural gas or coal together with carbon capture and storage. CO2-free ammonia synthesis is technology for synthesizing ammonia using such CO2-free hydrogen.
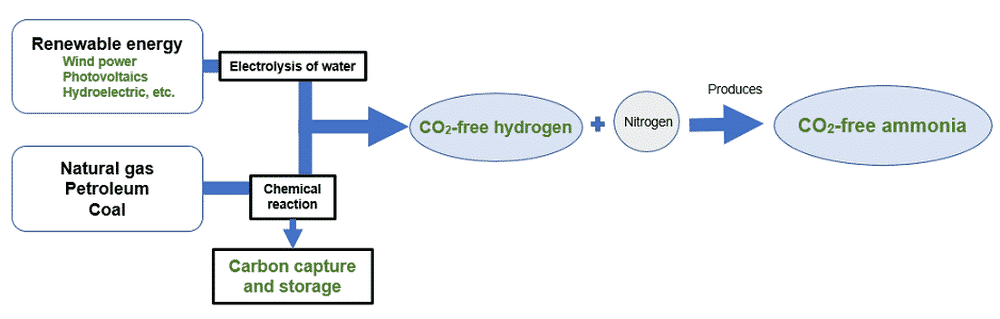
Image Credits: nyk.com
*** Four-stroke engine
An engine that performs the four basic processes (intake, compression, combustion/expansion, and exhaust) of a reciprocating engine while the crankshaft makes two rotations (the piston makes two reciprocating movements, that is, four strokes). The four-stroke engine is used for marine propulsion and power generation because it has a wide output range that can be handled by setting the bore diameter and rotation speed.
**** Two-stroke engine
An engine that burns once per rotation of the engine (one reciprocation of the piston) and is characterized by a small number of parts, light weight, and compactness. The two-stroke diesel engine installed as the main engine of a large ship is equipped with an exhaust gas turbocharger and has an ultra-long stroke structure, which achieves thermal efficiency of over 50% and low rotation / high output. It raises propeller efficiency and contributes to the energy-saving operation of ships.
Reference: nyk.com
Japan Gives Nod To Begin Demonstration For Vessels Equipped With Ammonia-Fueled Engine appeared first on Marine Insight – The Maritime Industry Guide
[ad_2]
This article has been posted as is from Source